retuple
| Name | Type | Description | Optional |
|---|---|---|---|
input |
?0 |
an input tuple |
no |
taken from tuple type |
taken from tuple type |
value to assign to the first slot |
yes |
taken from tuple type |
taken from tuple type |
value to assign to the second slot |
yes |
… |
|||
taken from tuple type |
taken from tuple type |
value to assign to the final slot |
yes |
| Name | Type | Description | Optional |
|---|---|---|---|
output |
?0 |
the modified tuple |
no |
retuple takes an input tuple, and an input value for each slot of the tuple. If a slot input port is unused, i.e., the input port is not connected to anything, then that slot of the input tuple is not modified; the original slot value is passed to the output. if the slot input is used, however, then it is assigned to that slot, overriding that slot in the input tuple. This is similar to the object.assign() operator in Javascript. See the example SpecialNodes/retuple:
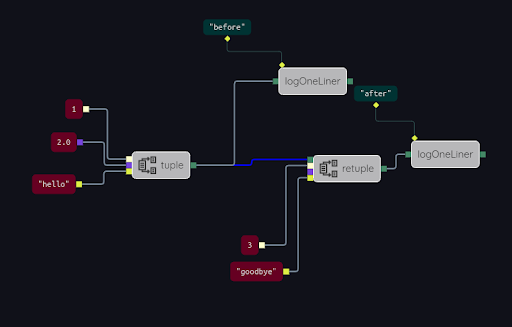
The result of running this example is this:

The input tuple to retuple (top input port) is {"a":1,"b":2,"c":"hello"}. two of the slots of this tuple –a and c– are overridden, assigned by the retuple operation. This is because two of the slot inputs to the retuple are connected. The third slot –b– is not overridden, its value in the original input tuple is preserved. In the result therefore the b slot has value 2.