switch
image:nodes/Special/SpecialNodes-switch.png[]
| Name | Type | Description | Optional |
|---|---|---|---|
case0 |
?0 |
case selector for out0 |
yes |
case1 |
?0 |
case selector for out1 |
yes |
… |
|||
case N-1 |
?0 |
case selector for out N-1 |
yes |
| Name | Type | Description | Optional |
|---|---|---|---|
selector |
?0 |
selector value |
no |
input |
?1 |
data to be routed to selected output |
no |
| Name | Type | Description | Optional |
|---|---|---|---|
out0 |
?1 |
output selected when case0 is matched |
yes |
out1 |
?1 |
output selected when case1 is matched |
yes |
… |
|||
out N-1 |
?1 |
output selected when case N-1 is matched |
yes |
switch reads its selector and input input ports. It compares the selector value to the case labels case0 through caseN-1. If the selector value is equal to casei, the input value is sent to the corresponding output outi. Otherwise the input value is sent to the default output if there is one. The default output is the output for which the corresponding case label is unused, i.e., has no incoming link. There can be at most one default output.
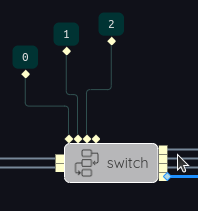
For example, in the case of the switch above, suppose the selector input is the integer 3. This value does not match any of the provided case labels (0, 1 and 2). There is however a default output – the final case label is unused and therefore identifies the corresponding (final) output as the default output. The input value is routed to the final output port, shown highlighted.
It is not required that there be a default output, but if there is one, there must be only one. Nor is it required that the default output be the last output. If we change the example above to this:
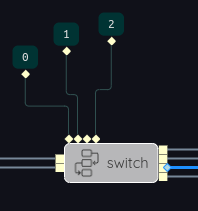
Then a selector value of 3 would cause the input value to be routed to the next-to-final output (shown highlighted).
It is strongly recommended that switch always be paired with a matching choose node, and that the conditional branches that are controlled by the switch / choose pair be placed in their own circuits, per the guidelines given in Dataflow in Coreograph (Conditionals).