collectset

| Name | Type | Description | Optional |
|---|---|---|---|
input |
?0 |
element to be added to the set |
no |
include |
?1 (interpreted as boolean) |
if true, add current input to the set |
yes |
complete |
?2 (interpreted as boolean) |
if true, output the accumulated set and reset the accumulator to the empty state |
no |
| Name | Type | Description | Optional |
|---|---|---|---|
output |
set<?0> |
the accumulated set, output when the complete input is true |
no |
collectset reads its three inputs ports. if include is true (or if the include port is not connected), the input is added to the accumulated set. if complete is true, the accumulated set is output, and the accumulator is reset to empty. Note that there is no output except when the complete input is true. It is recommended that you read the Iteration section of the Dataflow in Coreograph document in addition to the information presented here.
Let’s see what happens if we replace the collectlist operation in the last example by collectset (open the Special Nodes example collectset:
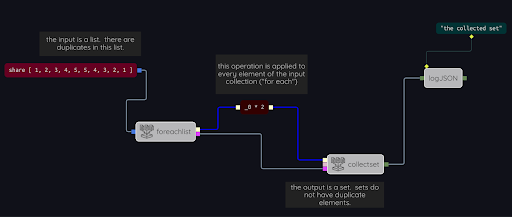
The collectlist operation has been replaced by collectset. Whereas a list may have repeated elements and is ordered according to the order in which elements are inserted,, a set has no repeated elements and is ordered by the value of the elements. If you Run the example you will see that there are only 5 elements in the resulting set, because there are only 5 distinct values in the input sequence 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 10, 8, 6, 4, 2: